Step 1: UX Audit
A usability audit focuses on a website’s ability to support key user goals and tasks users want to complete with accuracy, ease, and speed. It does not identify every problem that exists on the website—it’s not possible to fully anticipate what all users will do as they interact with the site.
The evaluations are firmly based on existing standards – not personal opinions. The result is a set of recommendations and level of effort.
This audit should not be considered a substitute for user testing.
The website should be tested with actual users, early during development and after any design changes, to check the design, identify additional problems, and suggest improvements. SessionCam and scroll depth tagging can help support this.
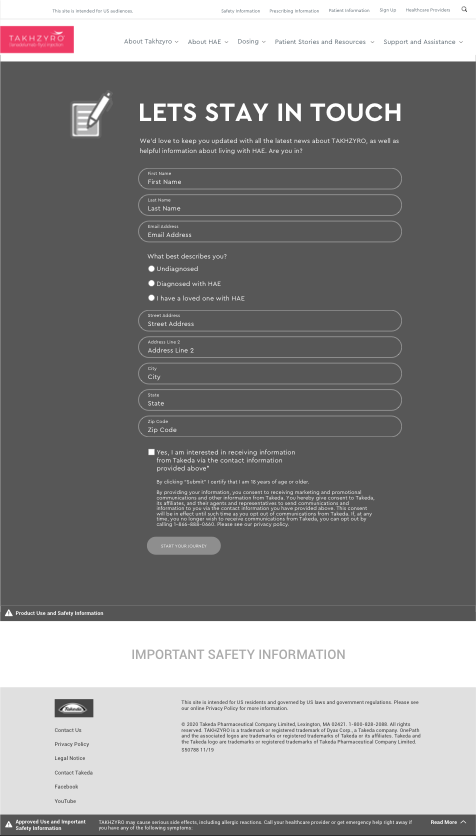
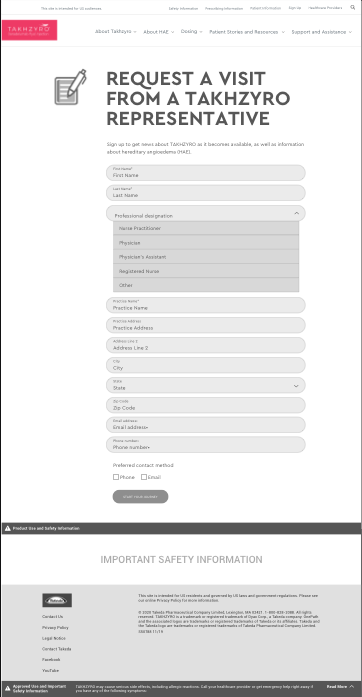
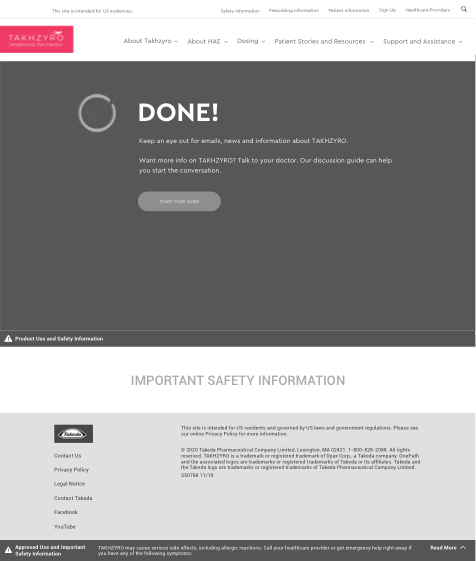
Get a UX Audit of Your Site!
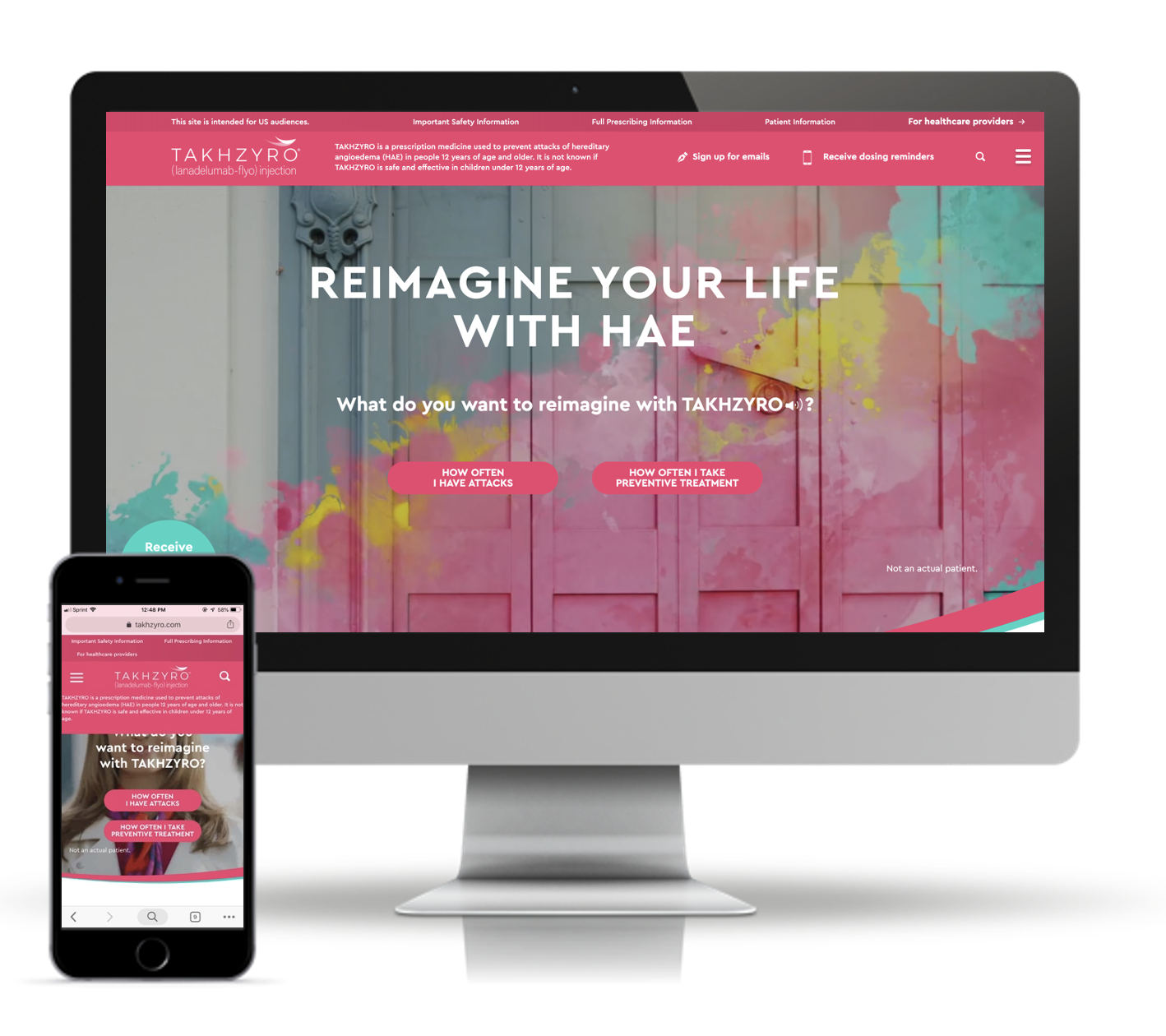


Step 2: User Flows.
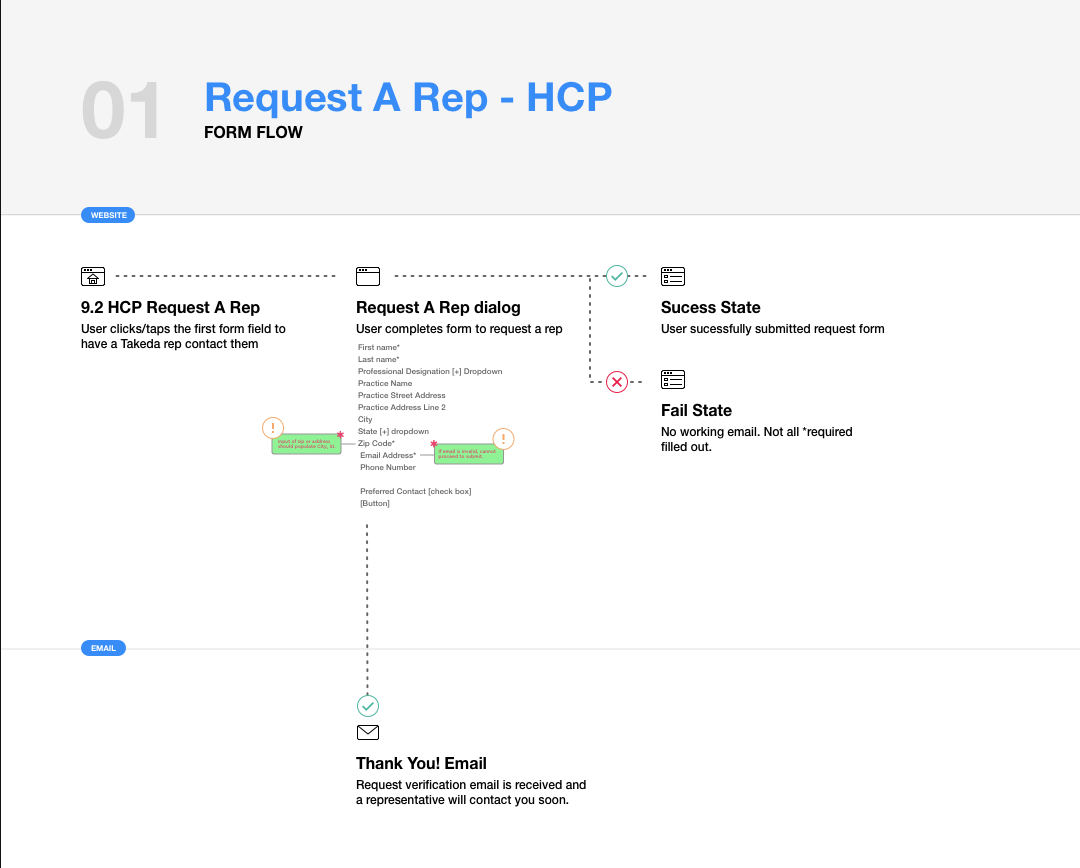
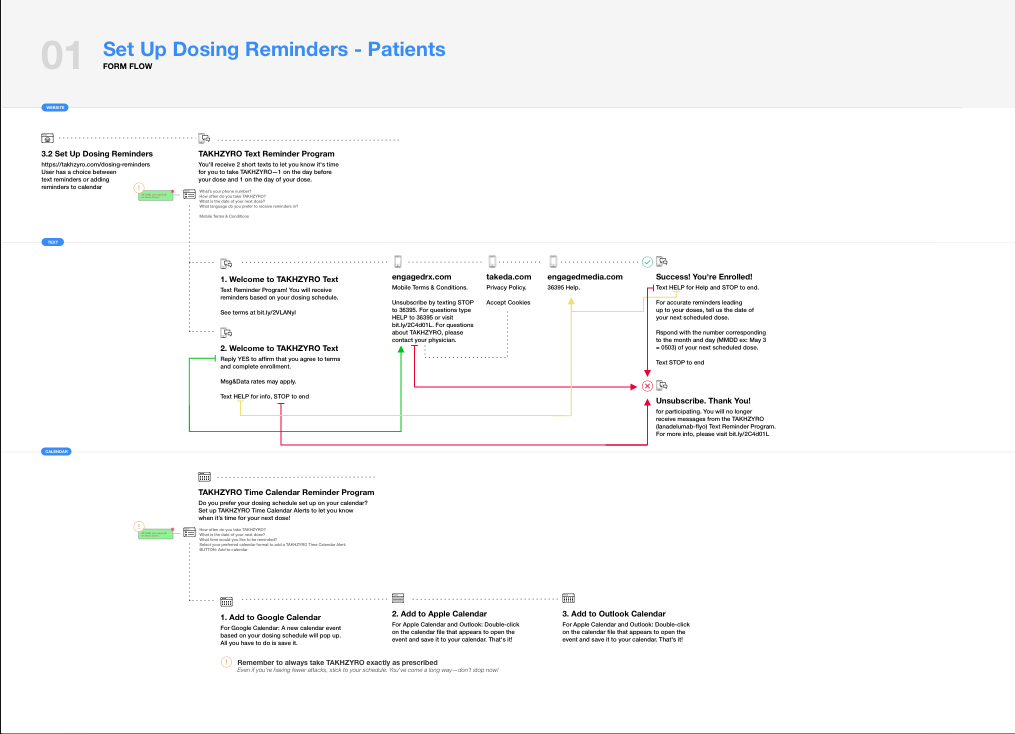
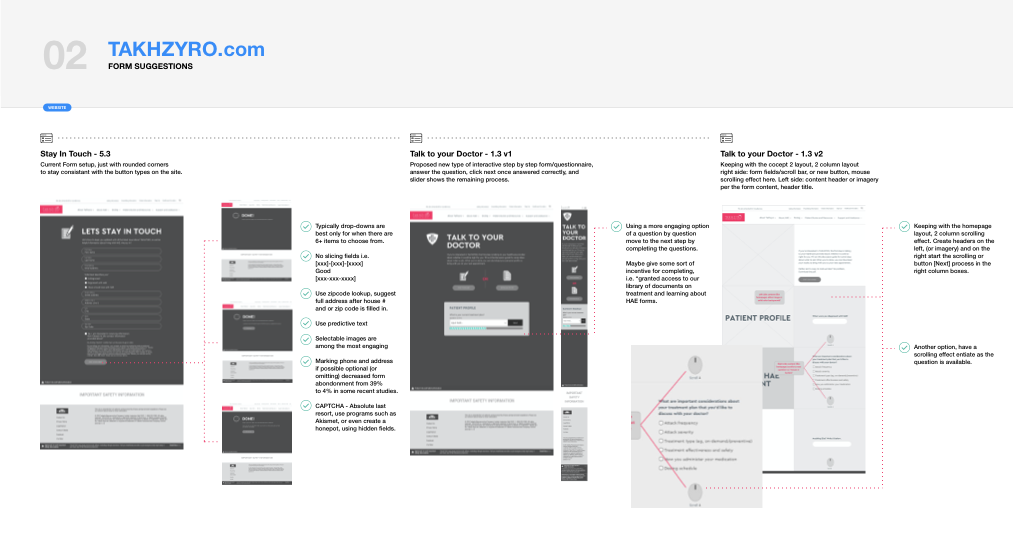
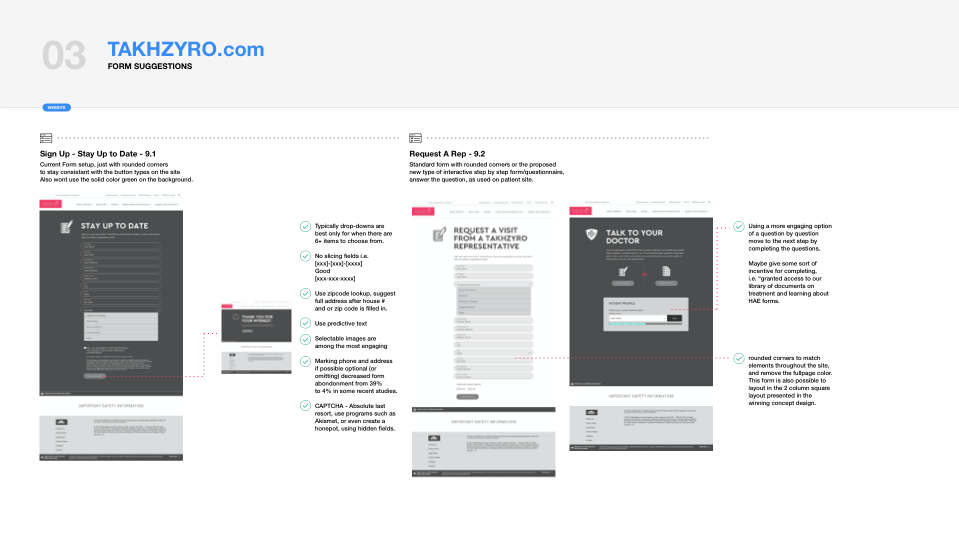
Information Architecture.
Information architecture (IA) is the organization, structuring and labeling of content to help users find information and complete tasks.
Good IA tells users where they are, what they’ve found, what’s available, and what to expect. Examples:
- Grocery store aisles
- Dewey Decimal System
- Websites
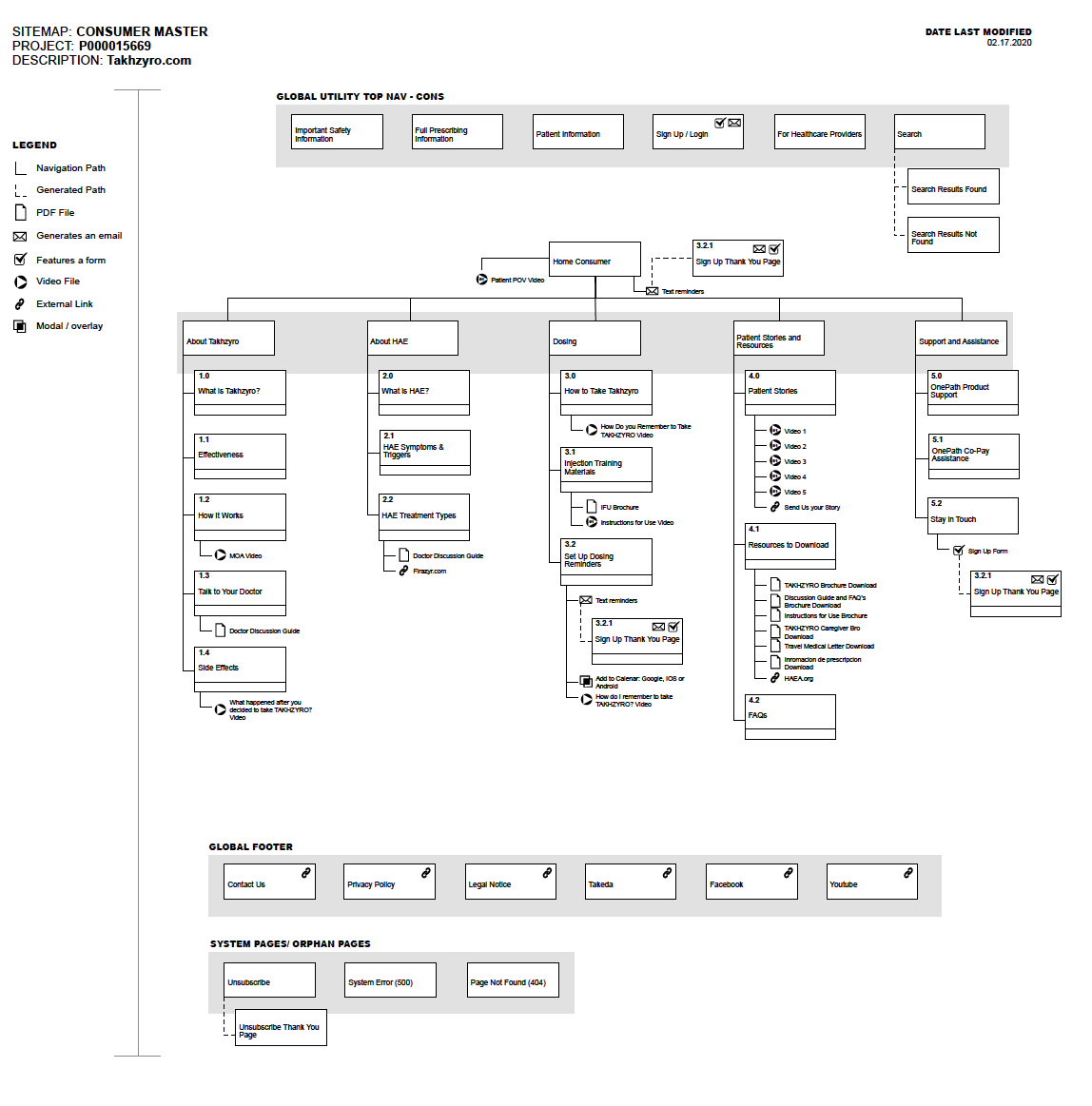
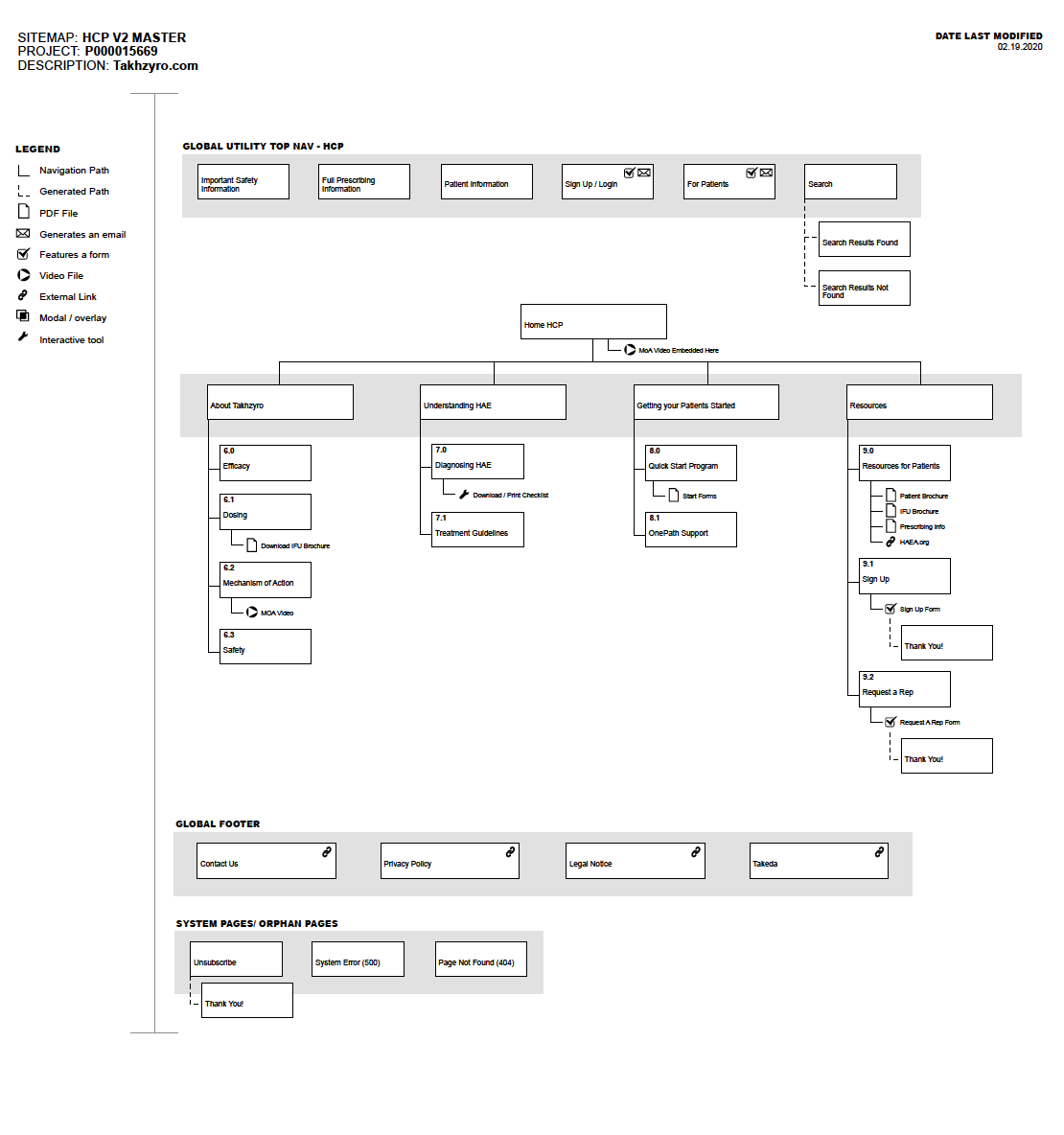
Site maps (shown below) are a hierarchical diagram that visualizes the information architecture of a website.
Wireframes.